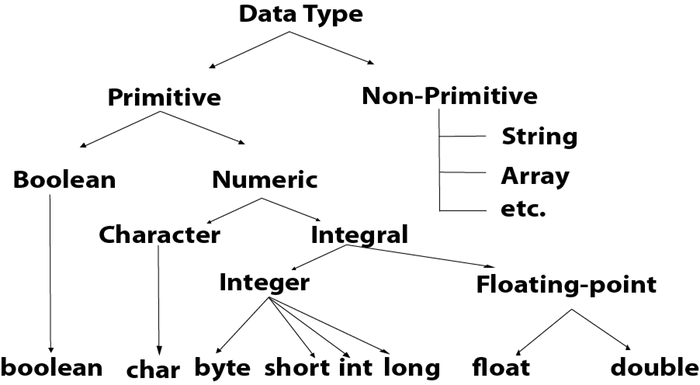
Data types specify the different sizes and values that can be stored in the variable. There are two types of data types in Java:
- Primitive data types: The primitive data types include boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float and double.
- Non-primitive data types: The non-primitive data types include Classes, Interfaces, and Arrays.
Java Primitive Data Types
In Java language, primitive data types are the building blocks of data manipulation. These are the most basic data types available in Java language.
Java is a statically-typed programming language. It means, all variables must be declared before its use. That is why we need to declare variable’s type and name.
There are 8 types of primitive data types:
- boolean data type
- byte data type
- char data type
- short data type
- int data type
- long data type
- float data type
- double data type
| Data Type | Default Value | Default size |
|---|---|---|
| boolean | false | 1 bit |
| char | ‘\u0000’ | 2 byte |
| byte | 0 | 1 byte |
| short | 0 | 2 byte |
| int | 0 | 4 byte |
| long | 0L | 8 byte |
| float | 0.0f | 4 byte |
| double | 0.0d | 8 byte |
Boolean Data Type
The Boolean data type is used to store only two possible values: true and false. This data type is used for simple flags that track true/false conditions.
The Boolean data type specifies one bit of information, but its “size” can’t be defined precisely.
Example:
Boolean one = false Byte Data Type
The byte data type is an example of primitive data type. It isan 8-bit signed two’s complement integer. Its value-range lies between -128 to 127 (inclusive). Its minimum value is -128 and maximum value is 127. Its default value is 0.
The byte data type is used to save memory in large arrays where the memory savings is most required. It saves space because a byte is 4 times smaller than an integer. It can also be used in place of “int” data type.
Example:
byte a = 10, byte b = -20 Short Data Type
The short data type is a 16-bit signed two’s complement integer. Its value-range lies between -32,768 to 32,767 (inclusive). Its minimum value is -32,768 and maximum value is 32,767. Its default value is 0.
The short data type can also be used to save memory just like byte data type. A short data type is 2 times smaller than an integer.
Example:
short s = 10000, short r = -5000 Int Data Type
The int data type is a 32-bit signed two’s complement integer. Its value-range lies between – 2,147,483,648 (-2^31) to 2,147,483,647 (2^31 -1) (inclusive). Its minimum value is – 2,147,483,648and maximum value is 2,147,483,647. Its default value is 0.
The int data type is generally used as a default data type for integral values unless if there is no problem about memory.
Example:
int a = 100000, int b = -200000 Long Data Type
The long data type is a 64-bit two’s complement integer. Its value-range lies between -9,223,372,036,854,775,808(-2^63) to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807(2^63 -1)(inclusive). Its minimum value is – 9,223,372,036,854,775,808and maximum value is 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. Its default value is 0. The long data type is used when you need a range of values more than those provided by int.
Example:
long a = 100000L, long b = -200000L Float Data Type
The float data type is a single-precision 32-bit IEEE 754 floating point.Its value range is unlimited. It is recommended to use a float (instead of double) if you need to save memory in large arrays of floating point numbers. The float data type should never be used for precise values, such as currency. Its default value is 0.0F.
Example:
float f1 = 234.5f Double Data Type
The double data type is a double-precision 64-bit IEEE 754 floating point. Its value range is unlimited. The double data type is generally used for decimal values just like float. The double data type also should never be used for precise values, such as currency. Its default value is 0.0d.
Example:
double d1 = 12.3 Char Data Type
The char data type is a single 16-bit Unicode character. Its value-range lies between ‘\u0000’ (or 0) to ‘\uffff’ (or 65,535 inclusive).The char data type is used to store characters.
Example:
char letterA = 'A' Why char uses 2 byte in java and what is \u0000 ?
It is because java uses Unicode system not ASCII code system. The \u0000 is the lowest range of Unicode system. To get detail explanation about Unicode visit next page.